INDUSTRY INFORMATION
PHONE:
Location:HOME INDUSTRY I... High-Frequency Electrosurgical Unit (ESU) Operating Procedures, Key Points, and Precautions
High-Frequency Electrosurgical Unit (ESU) Operating Procedures, Key Points, and Precautions
2025-05-12
High-frequency electrosurgical units, as indispensable medical devices in modern surgical procedures, utilize high-frequency electrical currents to achieve tissue cutting and coagulation functions, significantly enhancing surgical efficiency while reducing intraoperative bleeding. However, improper operation may pose safety risks. Simon?Medical will provide standardized guidelines for medical staff from the following aspects: usage protocols, key operational considerations, and medical personnel requirements.
?
I. Usage Protocols
Preoperative Preparation
Device Inspection: Ensure proper connections of the main unit, foot pedal, and electrode cables; verify the power supply is functioning properly; inspect disposable electrode pads for integrity.
Environmental Safety: Remove flammable materials (e.g., alcohol-soaked cotton balls) near the surgical bed; ensure the operating table is dry and the patient is insulated from metallic surfaces.
Electrode Pad Placement
Site Selection:
Apply electrode pads to muscle-dense areas near the surgical site (e.g., thigh, buttock) after shaving the area; ensure firm adhesion and a contact area?≥100 cm2.
Precautions:
Avoid placement near bony prominences or scar tissue to prevent current concentration and thermal injury.
Parameter Settings
Mode Selection:
Choose operating modes (Cutting/Coagulation) based on surgical type and tissue characteristics.
Initial Power Recommendations:
Cutting Mode: 40-60W (Note: Power output of Simon?Medical high-frequency electrosurgical units is adjustable in real time).
Coagulation Mode: 60-80W, adhering to the?"low-to-high" principle?for incremental adjustment.
Special Considerations:
Reduce power output for pediatric or debilitated patients to avoid excessive tissue damage.
Operational Testing
Pre-activation Check:
Perform a brief activation using?moist gauze?or a?dedicated test probe?to verify device functionality.
Verification Criteria:
Observe?spark intensity?and?auditory feedback?for normal operation;
Confirm?absence of alarm signals?or system abnormalities.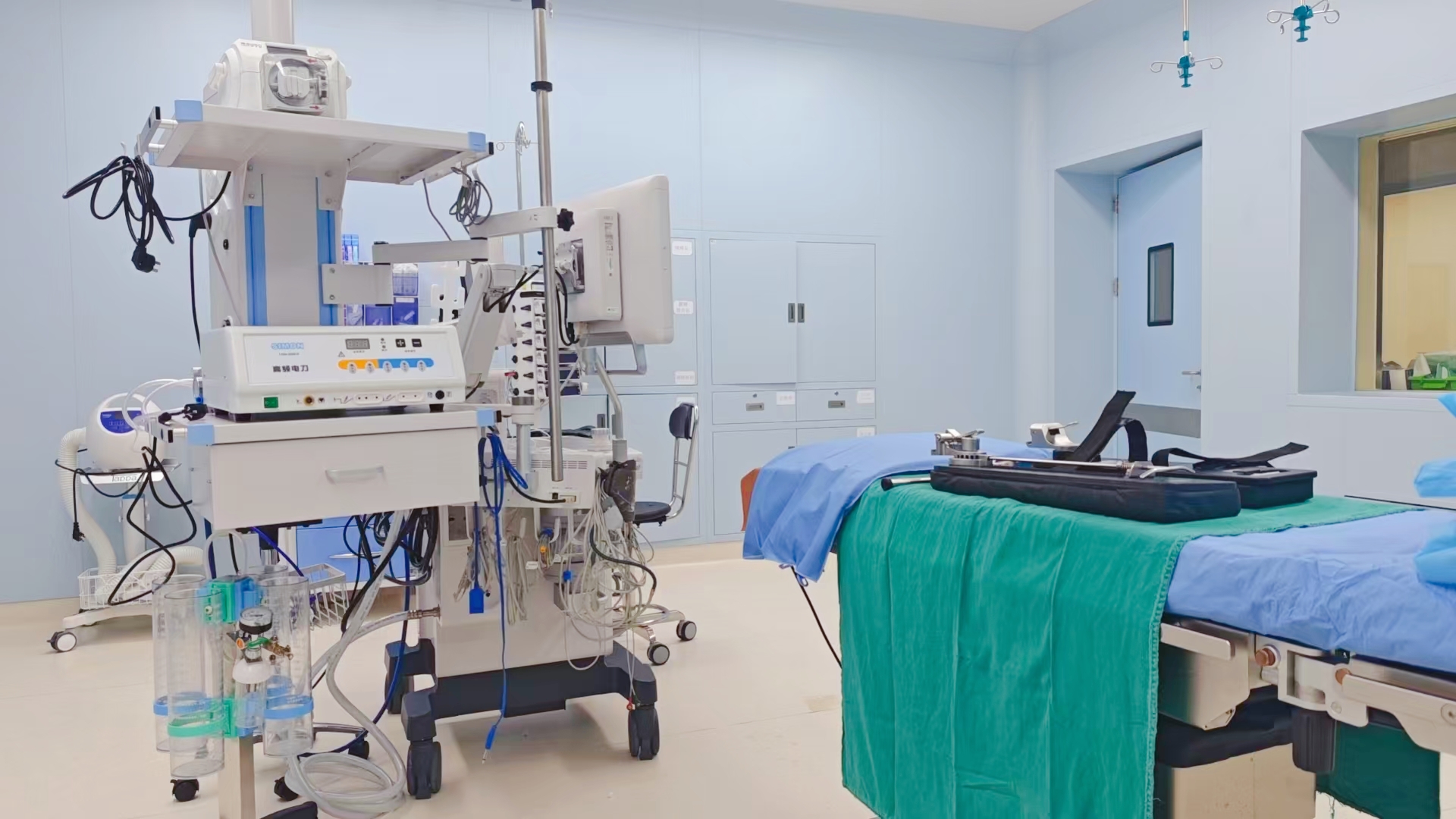
Postoperative Procedures
Device Shutdown:
Power off the device, remove electrode pads, and inspect the patient's skin condition?for signs of electrical burns or complications.
Equipment Maintenance:
Clean the cutting tip thoroughly, sterilize it, and store appropriately for future use;
Return the main unit to its designated storage location and?document operational parameters?for traceability.
?
II. Key Operational Guidelines and Risk Mitigation
Safety First
Fire Hazard Prevention:
Strictly prohibit use?in environments with flammable substances (e.g., alcohol). Electrosurgical sparks may ignite explosive vapors.
Patient Safety Protocols:
Ensure?complete insulation?between the patient and metallic surfaces to prevent?current diversion burns;
Never reuse disposable return electrodes?or reposition detached pads during procedures.
?
Power Adjustment Principles
Gradual Increment Protocol:
Always initiate at the lowest effective power?and incrementally increase following the?"low-to-high" principle?to minimize thermal tissue damage.
Special Tissue Considerations:
Increase power appropriately?when operating in deep tissues or fluid-rich environments (e.g., abdominal cavity) to maintain efficacy.
Intraoperative Monitoring
Device Alert Response:
Immediately suspend operation?upon triggering of alarms (e.g., poor contact, power overload) and?conduct systematic troubleshooting.
Patient Response Assessment:
Cease activation immediately?if abnormal muscle fasciculations or cutaneous erythema occur; verify circuit integrity and electrode contact.
?
Special Population Considerations
1. Absolute Contraindications
Cardiac Pacemaker Patients:
High-frequency electrosurgery is strictly contraindicated?in patients with implanted cardiac pacemakers. Electrosurgical currents may:
○ Disrupt pacemaker function;
○ Induce myocardial injury via pacemaker lead thermal transfer;
○ Potentially trigger?ventricular fibrillation.
2. Metallic Implant Precautions
For patients with retained/prosthetic metallic objects (e.g., shrapnel, orthopedic hardware, joint replacements, stents):
Electrode Placement Strategy:
○ Position return electrodes to establish current pathways?away from metallic implants;
Operational Modifications:
○ Utilize?lower power settings;
○ Limit activation duration;
○ Enhance heat dissipation protocols to prevent?eddy current-induced thermal injury.
3. Patient Positioning Requirements
Immobilize extremities?to prevent contact between body parts with differential electrical potentials, particularly?small-area contact points?which may concentrate current density and cause burns.
4. Pediatric Population
Mandatory Use?of?pediatric-specific electrode pads?with optimized contact geometry during infant/neonatal procedures.
III. Healthcare Personnel Requirements
1. Mandatory Training Standards
Qualification Prerequisite:
Operators?must undergo comprehensive training?demonstrating proficiency in:
○?Operational principles?of high-frequency electrosurgical units;
○?Standardized protocols?for device application and safety management.
2. New Device Implementation Protocol
Prior to using?newly introduced electrosurgical models:
Mandatory Documentation Review:
○ Thoroughly study?operation manuals?and?safety advisories?issued by Simon?Medical;
Preclinical Validation:
○ Conduct?full-functional testing?in non-clinical settings to verify performance parameters and alarm responsiveness.
?
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Requirements
Insulated Gloves:
Wear?high-integrity rubber gloves?with certified dielectric properties during all procedures.
Footwear Specifications:
Use?dry, thick-soled footwear?demonstrating verified electrical resistance to maintain grounding isolation.
Operational Safety Objective:
Ensure?continuous electrical isolation?from both grounded surfaces and the electrosurgical unit to establish?effective self-protection.
?
?
Summary
The clinical efficacy of high-frequency electrosurgical units (HF-ESU) is contingent upon?strict adherence to standardized protocols?and?meticulous execution of operational details. Medical personnel must:
Maintain?strict compliance with established procedures;
Exercise?enhanced intraoperative vigilance;
Implement?context-driven parameter optimization?to achieve?optimal surgical outcomes?while?maximizing patient safety.
Simon?Medical strongly recommends:
Periodic preventive maintenance programs?to ensure device reliability;
Mandatory operator competency training?to mitigate clinical risks and?maximize the therapeutic value?of electrosurgical systems.
?
Contact for technical support: 138-2067-8142
?
previous page: The use effect of microwave therapy equipment is very outstanding.
Next page: How much does a colposcope cost from the manufacturer?

Tel: 86 22-83712046/?83712048
Mobile: +86 166 2215 4239
???????????? +86 138 2067 8142
Email: tjsaimeng@126.com
Website: http://www.oynkfy.com
Address: Room 305-1, Building D, No. 6 Zhuyuan Road, Huayuan Industrial Zone, Tianjin